Cameras and plenty of different gadgets, together with smartphones and drones, have every kind of digicam sensor sizes. This text will attempt to make sense of the alphabet soup. And it’ll make it easier to perceive the impression of getting a bigger or smaller sensor.
The essential trade-off between a big and small sensor is picture high quality and comfort. Full body cameras swimsuit skilled photographers. And freshmen and fans typically favor crop sensor fashions.
The latter has smaller, lighter digicam our bodies and lenses and are typically cheaper. However nothing beats the comfort of a smartphone. The most effective digicam is at all times the one you could have with you!
What Are the Totally different Digital Digicam Sensor Sizes and Sorts?
There are lots of totally different sensor sizes. And even “customary” sensors usually have non-standard sizes and names! (Soar to the tip, the place we discuss sensor measurements and naming.)
For instance, many various variations of APS-C sensors exist. And Nikon’s crop sensor is a bit greater than Canon’s. The Nikon APS-C format (DX) crop issue is 1.5x, however Canon’s is 1.6x.
Drones have totally different sensor sorts relying on the scale. However 1″, 1/2″, 1/2.3″, or Micro 4 Third (MFT) sensors are frequent. GoPros have sensors of 1/2.3 or 1/1.9″ (GoPro Hero11 Black).
To make sense of all this, it’s most likely greatest to speak about and group the sensors by digicam kind. We’ll record them from smartphones to large-format cameras. We’ll record their specs, talk about their advantages, after which overview the professionals and cons of a bigger vs. small sensor.
1. Smartphone Digicam Sensor Dimension
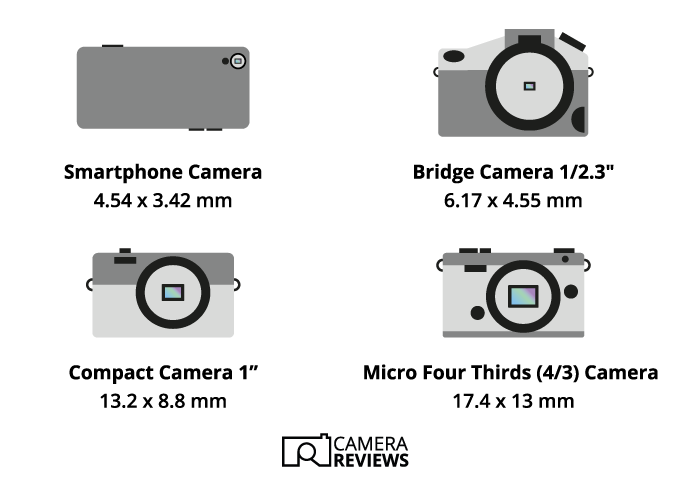
- Sort: 1/3.2″ (iPhone 5)
- Diagonal: 5.68 mm
- Dimensions: 4.54 x 3.42 mm
- Facet ratio: 4:3
- Space: 15.53 mm²
- Crop issue: 7.6x
Smartphones now have three totally different lenses and might take fairly good photos (and even 4K video!). However their sensors are tiny—particularly in comparison with full body sensors.
Totally different producers use totally different sensor sizes in numerous fashions. However they’re typically across the measurement of the 1/3.2″ sensor within the iPhone 5. This has a 4:3 facet ratio, which is typical of smartphone sensors. (Apple’s iPhone 14 has a 1/1.28″ sensor.)
Full body sensors have a facet ratio of three:2. However that may look a bit too “lengthy and skinny” in portrait format. It’s only a holdover from the times of 35mm movie, which occurred to have that specific facet ratio.
Smartphone sensors battle in low mild. However Apple has tried to enhance picture high quality by introducing up to date software program algorithms. These work fairly nicely. However smartphones won’t ever match the low-light efficiency of cameras with a lot bigger sensors.
2. Bridge Digicam Sensor Dimension
Bridge cameras (superzooms) have a hard and fast lens however an unlimited zoom vary. This makes them preferrred for close-ups or topics far-off. The “optical zoom” makes use of the whole sensor.
Nevertheless it must be small to get the loopy magnification doable with some bridge cameras. That’s since you’re successfully simply “zooming in” on what can be solely a small a part of the sensor on a full body digicam.
Once more, sensors differ relying on the actual producer and mannequin. However bridge digicam sensors typically have a 4:3 facet ratio.
Simply watch out for the “digital zoom.” That is usually marketed as a means of extending the zoom vary.
It really works by proscribing the scale of the energetic pixel space, which means picture high quality suffers. It’s significantly better to take photographs on the restrict of the optical zoom after which crop them later in post-processing.
3. Compact Digicam Sensor Dimension
- Sort: 1″ (Nikon CX sensor format, Sony RX10 IV, DJI Air S2, and so forth.)
- Diagonal: 15.86 mm
- Dimensions: 13.2 x 8.8 mm
- Facet ratio: 3:2
- Space: 116.16 mm²
- Crop issue: 2.7x
Compact cameras (or “point-and-shoots“) even have bigger sensors than superzooms. However they gained’t provide the similar magnification.
They once more have mounted lenses. And the comparatively small sensors permit them to be so “compact” that they simply slot in your purse or pocket.
Typical compact cameras have a facet ratio of three:2, like APS-C and full body cameras.
4. Micro 4 Thirds Sensor Dimension (Olympus)
- Diagonal: 21.64 mm
- Dimensions: 17.4 x 13 mm
- Facet ratio: 4:3 (however will be 3:2 or 16:9 on some fashions)
- Space: 226.2 mm²
- Crop issue: 2.0x
Olympus and Eastman Kodak initially invented the 4 Thirds sensor customary for DSLRs. Leica, Olympus, and Panasonic all produced digital digicam our bodies in that format. However the Micro 4 Thirds sensor has now changed it.
Panasonic and Olympus launched this format in 2008 for mirrorless cameras and camcorders. Now you can get digital digicam our bodies from a number of producers. However Olympus is the principle one.
Some of the helpful info concerning the Micro 4 Thirds customary is that it’s the smallest sensor in interchangeable-lens cameras. You solely get mounted lenses on smartphones, superzooms, and point-and-shoots.
This implies shopping for a Micro 4 Thirds system is costlier. Nevertheless it permits the pliability to make use of radically totally different focal lengths for landscapes or portraits, for instance.
The truth is, Olympus has a spread of Micro 4 Thirds cameras with subtle options. This contains the flagship Olympus OM-1.
It has a 20.4 MP sensor, topic monitoring, five-axis picture stabilization, 4K video, and IP53 mud and splash resistance. You’ll be able to even take 50 and 80 MP photos in Tripod Excessive Res mode.
5. Canon APS-C Sensor Dimension
- Diagonal: 26.8 mm
- Dimensions: 22.3 x 14.9 mm
- Facet ratio: 3:2
- Space: 332.27 mm²
- Crop issue: 1.6x
APS-C sensors have a 3:2 facet ratio. And they’re quite common, particularly amongst freshmen and intermediates.
The cameras and lenses are typically smaller, lighter, and cheaper than full body gear. However the APS-C sensor is greater than 60% smaller. So this makes it more durable to get high-resolution, noise-free photos for big prints.
Canon has a spread of round 20 variations of cameras with APS-C sensors. It contains the Canon EOS 90D, Canon EOS 7D Mark II, Canon EOS Rebel SL3, and Canon EOS Rebel T8i.

6. Nikon APS-C Sensor Dimension (DX)
- Diagonal: 28.8 mm
- Dimensions: 24 x 16 mm
- Facet ratio: 3:2
- Space: 384 mm²
- Crop issue: 1.5x
The Nikon equal of the APS-C sensor measurement is the DX format. It’s barely bigger than the Canon APS-C customary. However there’s no vital enchancment in picture high quality or noise discount.
7. Canon APS-H Sensor Dimension
- Diagonal: 34.2 mm
- Dimensions: 28.7 x 18.6 mm
- Facet ratio: 3:2
- Space: 533.8 mm²
- Crop issue: 1.3x
It is a barely bigger variation of Canon’s typical APS-C format. It appeared in varied variations of the Canon EOS-1D within the early 2000s. It was an try and profit from the corporate’s EF lenses, designed for full body sensor cameras.
It additionally meant the EOS-1D may shoot at 8 fps at a time when the complete body flagship mannequin (the EOS-1Ds) may solely handle 3 fps.
8. Full Body Sensor Dimension
- Diagonal: 43.27 mm
- Dimensions: 36 x 24 mm
- Facet ratio: 3:2
- Space: 864 mm²
- Crop issue: 1.0x
The total body format originated with 35mm movie. It took its identify from the width of the movie, together with the sprockets. It has nothing to do with the width of the body, which is 36 mm. That’s only a quite complicated coincidence!
Full body is the “gold customary” of recent cameras. Professionals use these cameras for each style of pictures, from portraits to wildlife. Though it’s not the most important digicam sensor measurement, it’s the most well-liked.
It hits the “candy spot” between picture high quality and different options. The total body sensor is sufficiently big to offer the decision each amateurs and execs want. Nevertheless it’s additionally sufficiently small to permit quick body charges.
Most photographers aspire to personal full body cameras sooner or later. However these are way more costly than Micro 4 Thirds or APS-C fashions. That’s an inevitable trade-off, given the bigger sensor and all of the accompanying electronics.
However the mirrorless revolution reveals it’s doable to make smaller full body digicam our bodies and lenses. This implies increasingly cash is being poured into mirrorless cameras and fewer and fewer into DSLRs.
One wildlife photographer I do know is nearly being “pressured” into going mirrorless. It is because his current DSLRs won’t ever be upgraded!
9. Medium Format Sensor Dimension
- Diagonal: 54.78 mm (e.g., Fujifilm GFX100)
- Dimensions: 43.8 x 32.9 mm
- Facet ratio: 4:3
- Space: 1,441.02 mm²
- Crop issue: 0.8x
Medium format cameras have massive 4:3 sensors. However they are usually greater and heavier than full body fashions with decrease body charges.
They’re additionally way more costly. That’s effective if you happen to’re an expert panorama photographer. Nevertheless it’s not handy sufficient to turn out to be standard.
10. Massive Format Sensor Dimension
- Diagonal: 150 mm
- Dimensions: 90 x 120 mm
- Facet ratio: 4:3
- Space: 10,800 mm²
- Crop issue: 0.3x
You’ll be able to decide up a lightweight Intrepid 4×5 digicam for just a few hundred {dollars}. However massive format movie and digital cameras are typically solely used for specialist functions.
These embody billboard advertisements, effective artwork pictures, and scientific imaging. The size imply you possibly can print photos in a lot bigger sizes. A big format can also be preferrred for revealing richer tones and the best ranges of element.
Execs and Cons of a Massive Sensor vs Small Sensor
There are 4 advantages to a bigger sensor:
You additionally get much less depth of field for a given discipline of view. This can be good if you wish to isolate your topic.
 Shot at f/2.8 for a shallow depth of discipline. © Nick Dale
Shot at f/2.8 for a shallow depth of discipline. © Nick Dale
A bigger sensor can squeeze in additional of them for any pixel measurement (photosite or sensel). That’s what gives the additional decision.
However you need to commerce off decision in opposition to low-light efficiency and dynamic vary. Decision depends upon the variety of pixels. However the different attributes rely on the pixels’ measurement.
In different phrases, if you happen to stuff as many pixels onto the sensor as doable, the pixels are smaller. So that you get extra noise and fewer element in highlights and shadows.
The identical occurs if you happen to put the identical variety of pixels from a big sensor on a smaller one. Much less space means smaller pixels. So that you get extra noise and fewer dynamic vary on a small sensor.
However there’s a worth to pay for bigger sensors. Silicon sheets price hundreds of {dollars}. And you’ll’t get as many full body sensors from every sheet due to their measurement. So this makes bigger sensors way more costly.
Magnification (Crop Issue) With Smaller Sensors
Smaller sensors do have some benefits. They successfully “zoom in” on the picture projected onto the again of the digicam. So that you don’t want such lengthy lenses to get the identical magnification.
One option to measure this additional magnification is utilizing the “crop issue.” That is merely the quantity you get once you divide the diagonal size of a full body sensor (36 x 24 mm, or 43.27 mm from nook to nook) by that of one other sensor.
Should you multiply a lens’s focal size by the crop issue, you get the “efficient” focal size on a full body digicam. Let’s take the instance of a 200mm lens on a Micro 4 Thirds (MFT) digicam with a crop issue of two.0x.
The efficient focal size will likely be 200 x 2 = 400mm. Meaning objects will seem a lot nearer and, thus, bigger. That is helpful for taking photos of small and distant objects.
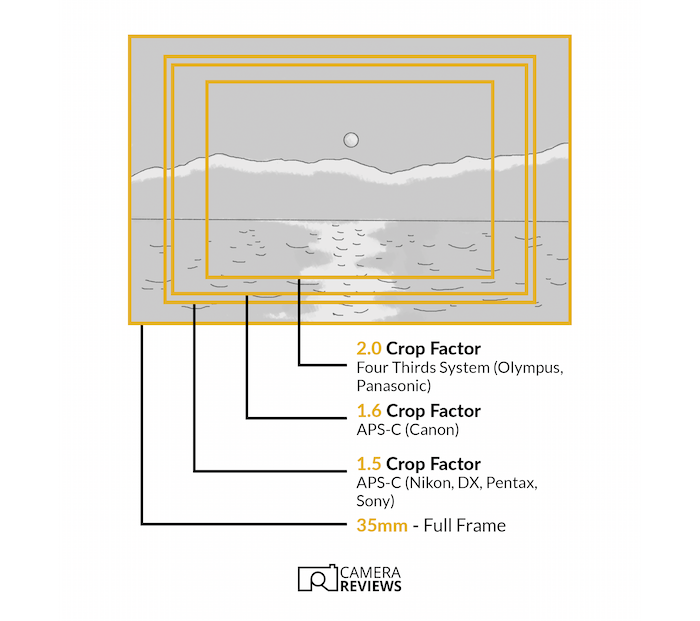
Right here’s one other means of taking a look at it. We are able to have a look at two photographs.
One taken with a Micro 4 Thirds digicam at 200mm and one other with a full body digicam at 400mm would have the identical discipline of view. In different phrases, on the similar distance, the framing can be precisely the identical.
However the crop issue isn’t an excellent information to the scale of every sensor. This measures the relative size of the diagonal. Nevertheless it’s the realm of the sensor that actually issues. Should you double the scale, you need to multiply the realm by 4.
A Micro 4 Thirds sensor could have a crop issue of two.0x. However its space is simply 226.2 mm² in comparison with 864 mm² for full body sensors. Meaning a full body sensor is nearly 4 occasions as massive!
Smaller Sensors Means Smaller Lenses
One other good thing about a smaller sensor is that the lenses don’t need to be as massive and heavy. Due to the narrower discipline of view, mild from the sides of a full body lens gained’t attain the sensor.
As soon as producers knew they may save on glass, they began making lenses that solely labored on crop-sensor cameras. Totally different corporations use totally different letters, however listed here are a number of the primary ones:
- Canon: EF-S, EF-M
- Nikon, Tokina: DX
- Pentax: DA
- Samsung: NX
- Sigma: DC
- Sony, Konica Minolta: DT, E
- Tamron: Di II
 Small, light-weight Canon EF-M 22mm f/2.0 STM prime lens for Canon APS-C cameras
Small, light-weight Canon EF-M 22mm f/2.0 STM prime lens for Canon APS-C cameras
Small Sensor’s Quick Body Price vs Massive Sensor’s Decision
Lastly, crop sensors produce smaller picture information. In order that they take much less time to write down to the reminiscence card. This implies cameras can have a better body price and deeper buffer—if you happen to’re prepared to compromise on decision and noise efficiency.
There’s at all times been a trade-off between decision and body price. And only a few producers have been in a position to keep away from it. However readout speeds are enhancing on a regular basis.
The Sony a1 mirrorless digicam can nonetheless shoot at 30 fps in a lossy, RAW format though it has a 50.1 MP sensor. It’s solely a matter of time earlier than Nikon, Canon, and different producers make the identical technological advances.
The enhancements needs to be accessible in flagship fashions within the subsequent couple of years. They might even flip up inside reasonably priced cameras for fans and freshmen.
Sensor Measurements (Making Sense of Their Names)
Some of the complicated issues about sensors is their names. Why are some measured in inches (“) and others in millimeters (mm)? Why have they got totally different facet ratios?
What does APS-C stand for? What sort of a fraction is 1/3.2″? Why aren’t 1” sensors one inch large?
A brief reply is that lots of of corporations worldwide designed their very own sensors. This meant all of them had their very own business and cultural imperatives.
For instance, US corporations used imperial items (inches). And European corporations used the metric system (millimeters).
 Cleansing a digital digicam sensor with a sensor cleaning kit
Cleansing a digital digicam sensor with a sensor cleaning kit
The three:2 facet ratio additionally got here from a historic accident. It simply occurred to be the facet ratio of 35mm movie. So digital cameras “borrowed” it to take care of a uniform body measurement.
And APS is an abbreviation for Superior Photograph System. This movie format was designed in 1996 by Eastman Kodak, Fujifilm, Agfa, and Konica. So there have been three sizes:
- H for Excessive Definition was 30.2 x 16.7 mm with a facet ratio of 16:9 (1.25x crop)
- C for Traditional was 25.1 x 16.7 mm with a facet ratio of three:2 (1.44x crop)
- P for Panoramic was 30.2 x 9.5 mm with a facet ratio of three:1 (1.36x crop)
Fashionable digital cameras nonetheless use APS-C and APS-H sensors. However the actual measurements differ by producer.
Why an Optical Format is Used
One other historic accident is utilizing “optical” format names for sensors utilizing fractions and inches. A number of smaller sensors have been invented within the ’50s, ’60s, ’70s, and ’80s.
And vacuum tubes have been used quite than CCD or CMOS sensors in video and TV cameras. Every tube was spherical and product of thick glass. And the picture was a smaller rectangle inside that round cross-section.
The picture sensor measurement was taken from the outer diameter of the tube. And it conveniently made the sensor sound 50% greater than it really was!
Therefore, the 4/3″ or 4 Thirds sensor is simply 0.85″ (or 21.64 mm) from nook to nook. Nevertheless it takes its identify from a tube that needed to be 4/3″ (or 33.9 mm) large.
Conclusion
The proliferation of digicam sensor sizes over the previous couple of years has confused many individuals. There are lots of sorts of cameras, from smartphones to large-format cameras. They usually all use totally different sensors—usually with unusual names!
Should you’re seeking to purchase a brand new digicam, you could possibly simply spend hours and hours evaluating the totally different codecs. However the trade-off is basically easy—it’s decision vs comfort.
Have a look at your present wants and funds. And determine what’s greatest for proper now. I began with a bridge digicam. Then I moved on to a full body DSLR digicam. And eventually, I switched to mirrorless cameras. You’ll be able to most likely skip the DSLR, however everybody will take a distinct path.
 Smartphone digicam lenses and sensor
Smartphone digicam lenses and sensor
Massive Sensor Sizes vs Small Sensor Sizes
Bigger sensors imply bigger digicam our bodies and lenses, that are much less transportable and costlier. Mirrorless, interchangeable-lens cameras are typically smaller and lighter than DSLRs. However they’re greater than most compacts and superzooms (bridge cameras).
Crop sensor fashions boast huge zoom ranges and excessive body charges. However bigger codecs supply higher picture high quality. The depth of discipline is shallower (for a given discipline of view), which portrait and wildlife photographers recognize.
You additionally get greater decision and higher low-light efficiency, notably at excessive ISOs. However there’s a trade-off right here, too. Should you pack the sensor with pixels, the pixel pitch will get smaller. This reduces the light-gathering capability. And it means extra noise and fewer dynamic vary.
We hope our article has helped you become familiar with understanding totally different digicam sensor sizes! To proceed studying about pictures fundamentals, take a look at posts on the totally different elements of a digicam or DSLR vs mirrorless for freshmen. We’ve some nice shopping for guides on snowboarding cameras or nature pictures cameras to take a look at too!